Using this web page
hide
- Click the BRUS3QR (Bru-seeker) icon to show these instructions.
- Click on a miRNA name to the left to display its data images.
- Use the View menu above to determine which data will be displayed.
- Search for a specific miRNA by typing its name in the box.
- Use the Filter menus to further restrict the miRNA list. Hover
over a menu for more information.
- Hover over a transcript annotation or heat map to see the gene or cell line.
Understanding the images
hide
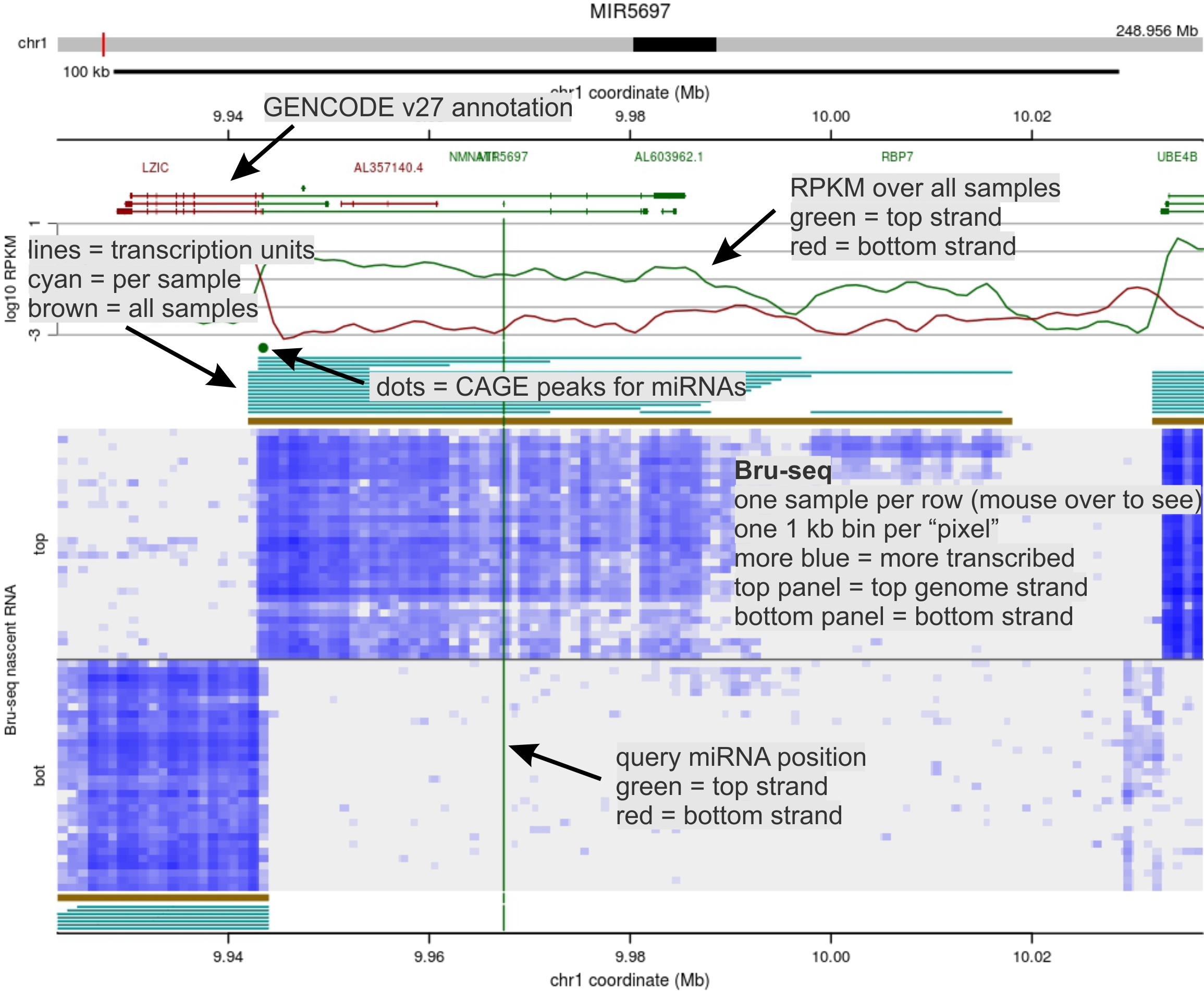
Bru-seq (32 cell lines)
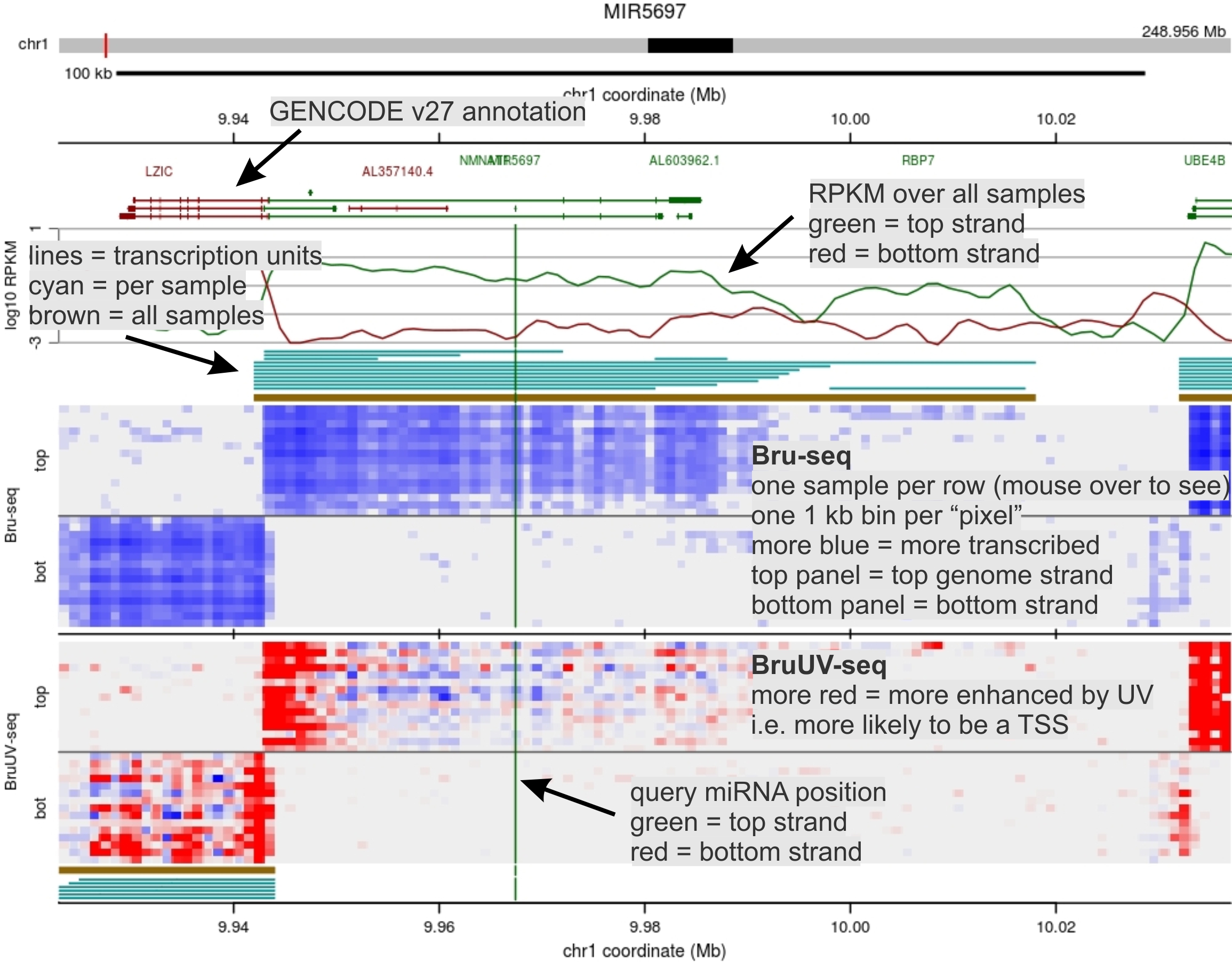
Bru-seq + BruUV-seq (15 cell lines)
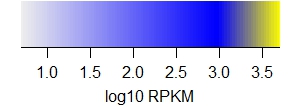
The following legends demonstrate the heat map colors.
Note that
(i) values are in log10 RPKM,
(ii) outlier values use the extreme colors
(iii) RPKM plots saturate (yellow color),
(iv) BruUV-seq is a difference plot (BruUV - BrU), and
(v) expressed miRNAs achieve very high RPKM.
| Bru-seq |
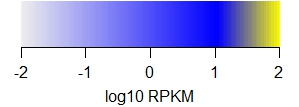 |
| BruUV-seq |
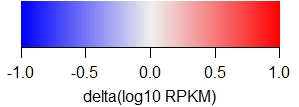 |
| miRNA-seq |
 |
Overview of miRNA transcription
hide
This page shows nascent transcription data using the Bru-seq
suite of methods to reveal human primary microRNA (pri-miRNA) transcripts, or
transcription units.
A transcription unit (TU) is the longest span of the human genome (GRCh38/hg38) traversed
by a single transcribing RNA polymerase molecule to yield a transcript that
contains the miRNA. Whether the miRNA is ultimately expressed is determined
by downstream processing and turnover, but
a pri-miRNA must be synthesized for the miRNA to be expressed.
pri-miRNA transcription units are critical regulators of miRNA expression
as they define the promoter and termination elements that control
transcription, which can vary considerably between transcript isoforms,
cell types, etc.
miRNAs can be transcribed as part of protein-coding or long non-coding RNA genes,
or from their own transcription units (called intergenic). Because
a miRNA is processed independently of any coding exons it
can reside outside the annotated boundaries of a gene,
e.g. in the region 3' to the polyadenylation site where transcription
continues as part of mRNA maturation. This can place miRNAs on
the opposite strand of an adjacent gene. These and other features add to the
complexity of miRNA transcriptional control.
Sequencing methods
hide
Bru-seq uses a pulse of bromouridine (Bru) to label RNA undergoing synthesis
in a cell. Labeled material is subjected to high throughput sequencing. Reads
map to the genome where an RNA polymerase was actively synthesizing RNA,
revealing transcription units (very different than standard RNA-seq).
This page show Bru-seq data from 32 diverse human cell lines (see below).
BruUV-seq is like Bru-seq, except that cells are first irradiated with
ultraviolet (UV) light to create DNA lesions that block RNA polymerases. The
read signal thus accumulates just downstream of transcription start sites (TSSs),
helping to clarify the span of transcription units. This page show BruUV-seq data
from 15 of 32 cell lines.
miRNA-seq uses size selection and other methods to only sequence small RNAs
expressed in cells. All miRNA-seq data depicted here were obtained from
the ENCODE project.
This page show miRNA-seq data from 4 of 32 cell lines.
Cell lines
hide
Here is a complete list of the 32 human cell lines summarized on this page:
A2058
A375
A673
BxPC3
HF1_CSB
GM12878
GM12891
HAP1
HCT116
HEK293
Hep3B
HepG2
HME
HPDE
HPNE
iPSC
K562
MCF7
MiaPaCa
HF1
panc1
SHEP1
T-47D
U2OS
U87
UM5
UC9
UM16
UM28
UM59
UML49
HF1_XPC
Citing this work
The publication reporting this work is in preparation. For now, please reference:
Characterization of novel primary miRNA transcription units in human cells using Bru-seq nascent RNA sequencing
Karan Bedi, Michelle T. Paulsen, Thomas E. Wilson and Mats Ljungman
University of Michigan Medical School
You may use any image obtained from this website as long as you cite and acknowledge its source.




